You get to the menu navigating in the project tree to a subbranch of Audio System.Super Output Functions are DSP functions universally applicable for switching, level, talkback and summation applications. Often, these functions are used directly in front of audio outputs of the RM4200D. In general, they work similar to the related Output Functions, where the name “Super Output Function” originates. They are mainly used when several signals are to be coupled at the same time. (see also Output Functions)
Super Output Functions are able to sum up to 16 input sources (Input 1-16) per function. Each input source is treated equally and can be modified individually depending on logic Conditions. The output signal of a Super Output Function itself is available to the TDM bus as audio source.
![[Important]](../pics/important.gif) | Important |
|---|---|
Each DSP Module RM420-848 can supply a maximum of 6 Super Output Functions. This adds up to a total number of 18 possible Output Functions per DSP Frame. Therefore, use the Super Output Functions carefully to avoid complex cascades of Output Functions. | |
You can use the following signals as input signals (Source):
Audio channels available on the TDM bus: inputs, mixing (summations, groups, Aux busses), Pre Fader (Fader Channel after Input Processing), Clean Feed (n-1 busses), Monitor Functions (PFL only), Fixed Processing, Output Functions.
Internal “virtual” audio sources: Monitor Functions (Monitor busses 1 - 6, Rotary Monitor Selector 1 - 10), Routing (number 1 to 768).
You can set the label values (Level) between -oo (off), -100 dB to +20 dB in increments of 1 dB. Furtheron, to this set amplifier value, the value of a potentiometer can be added and the phase orientation of the signal can be turned by 180˚.
Overall, a Super Output Function can have up to 4 further logic functions besides the preset Logic Condition None. Each of them is displayed in the right pane of the dialog as line in the list, it can have assigned different input signals and level values.
The logic condition None is always listed in the first line and is always active if none of the configured conditions underneath is active (logically true).
You can use all logic sources available in the Logic Sources Window as logic conditions in the column Condition.
The priority of the logic conditions decreases from top to bottom, therefore a condition is only used if all conditions above are inactive.
![[Important]](../pics/important.gif) | Important |
|---|---|
Super Output Functions are mono in their inputs as well as their outputs. For stereo signals, they have to be programmed separately for the left and the right channels! | |
To create a new Super Output Function, click on the button at the bottom of the Super Output Functions list; to delete a Super Output Function, click on the button respectively. You can also access both functions using the context menu in the list Super Output Functions.
![[Note]](../pics/note.gif) | Note |
|---|---|
To be able to use Super Output Functions as inputs for Stereo Fader Channel or for Stereo Fixed Processing, there has to be always a even number of Output Functions in front of the Output Function with the left channel. For Output Functions that are used as paired stereo, the right channel must follow the corresponding left channel. | |
![[Warning]](../pics/warning.gif) | Warning |
|---|---|
You should never delete Output Functions when modifying a configuration, since otherwise the assignment of the following Function Pairs is disturbed when they are used as stereo inputs for Fader Channels or fixed processing! Assign the unused Output Functions a new name instead, e.g. “unused1” or “rem”. The Output Functions marked as unused this way can be reused later on. | |
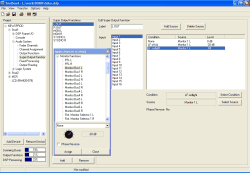
In the dialog Edit Super Output Functions you can configure the properties of the Super Output Function highlighted on the left side in the Super Output Functions list.
The configure a newly added Super Output Function, do the following:
Apply a descriptive name to the Super Output Function, to do this, use the text field Label. This name may be up to 10 digits long. Please be aware that for a maximum of 18 available Super Output Functions per Device, the selection of a suitable name can be vital for the clarity of the Config.
In the list Input highlight the input you want to configure.
Insert a new condition line for this new input; to do this, use the button . Now highlight the line that you want to modify. The two buttons under the list become active.
Click on the button to open or activate the Logic Sources Window. Select the desired logic source and assign it using the button . Alternatively, you can drag the logic source directly to the desired position in the first column of the list. The first line does always contain the condition None, this can not be changed.
Assign the Audio Sources for the selected line. To do this, click on the , to open or activate the Audio Sources Window. Now select the desired source and use the potentiometer in the Audio Sources Window to set the level. To modify the level, click and hold the potentiometer knob. If you now move the cursor with held mouse key to the left and to the right, you can modify the level. Alternatively, you can also click on the knob, hold the mouse key and change the set value using the following cursor keys:
+ 1 dB increments Arrow right or Arrow up - 1 dB increments Arrow left or Arrow down Off Pos 1 + 20 dB End + 10 dB increments Page Up - 10 dB increments Page Down To change the phase orientation of the selected audio source by 180 degrees, activate the Phase Reverse checkbox.
In the Audio Sources Window, there is a popup menu with potentiometers as well. Here you can select a potentiometer, the level value of which becomes effective in addition to the configured value. If e.g. you have set the level of the audio source to -3dB and the selected potentiometer is set to -15 dB, the signal is attenuated by a total of -15dB + (-3dB) = -18dB. Select the desired potentiometer or use the None entry, if you do not want to use any potentiometer.
The functions described in the section Potentiometer are available as potentiometers, and also for the Global Potentiometers 1 to 20. (see also Potentiometers )
Global Potentiometers can be set either by a fader of one of the Devices defined in the project or using a script. (see Channel Assignment – Assigning Fader Channels and DSP Processing)
In the list Inputs select one or more further inputs and configure them accordingly.
You can also use the following opportunities when configuring the Output Functions:
Use the button to remove a whole condition line.
Using the context menu, the functions Insert Source, Select Condition, Select Source, Set Level Off and Remove Source can be carried out for the marked line respectively. Set Level Off sets the level to -100 dB, i.e. “Off”.
By double clicking on the corresponding column, you can directly configure the conditions as well as the audio sources for the marked line.
You can modify the priorities of the conditions by simply dragging an dropping the list entries.